Data Update 6 for 2025: From Macro to Micro - The Hurdle Rate Question!
-
In business investing (capital budgeting and acquisition) decisions, it becomes a hurdle rate for investing, where you use it to decide whether and what to invest in, based on what you can earn on an investment, relative to the hurdle rate. In this role, the cost of capital is an opportunity cost, measuring returns you can earn on investments on equivalent risk.
- In business financing decisions, the cost of capital becomes an optimizing tool, where businesses look for a mix of debt and equity that reduces the cost of capital, and where matching up the debt (in terms of currency and maturity) to the assets reduces default risk and the cost of capital. In this context, the cost of capital become a measure of the cost of funding a business:
- In dividend decisions, i.e., the decisions of how much cash to return to owners and in what form (dividends or buybacks), the cost of capital is a divining rod. If the investments that a business is looking at earn less than the cost of capital, it is a trigger for returning more cash, and whether it should be in the form of dividends or buybacks is largely a function of what shareholders in that company prefer:
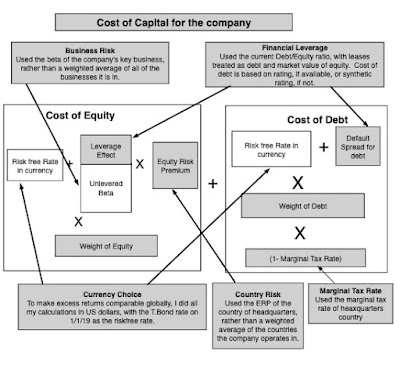
- The first is, of course, the riskfree rate, a number that varies across time (as you saw in post on US treasury rates in data update 4) and across currencies (in my post on currencies in data update 5).
- The second set of inputs are prices of risk, in both the equity and debt markets, with the former measured by equity risk premiums, and the latter by default spreads. In data update 2, I looked at equity risk premiums in the United States, and expanded that discussion to equity risk premiums in the rest of the world in data update 5). In data update 4, I looked at movements in corporate default spreads during 2024.
-
Relative Equity Risk, i.e., a measure of how risky a company’s equity is, relative to the average company’s equity. While much of the discussion of this measure gets mired in the capital asset pricing model, and the supposed adequacies and inadequacies of beta, I think that too much is made of it, and that the model is adaptable enough to allow for other measures of relative risk.I am not a purist on this measure, and while I use betas in my computations, I am open to using alternate measures of relative equity risk.
- Corporate Default Risk, i.e, a measure of how much default risk there is in a company, with higher default risk translating into higher default spreads. For a fairly large subset of firms, a bond rating may stand in as this measure, but even in its absence, you have no choice but to estimate default risk. Adding to the estimation challenge is the fact that as a company borrows more money, it will play out in the default risk (increasing it), with consequences for both the cost of equity and debt (increasing both of those as well).
-
Operating geographies: The equity risk premium for a company does not come from where it is incorporated but from where it does business, both in terms of the production of its products and services and where it generates revenue. That said, the status quo in valuation in much of the world seems to be to base the equity risk premium entirely on the country of incorporation, and I vehemently disagree with that practice:Again, I am flexible in how operating risk exposure is measured, basing it entirely on revenues for consumer product and business service companies, entirely on production for natural resource companies and a mix of revenues and production for manufacturing companies.
- Riskfree rate: To allow for comparisons and consolidation across companies that operate in different currencies, I chose to estimate the costs of capital for all companies in US dollars, with the US ten-year treasury rate on January 1, 2025, as the riskfree rate.
- Equity Risk Premium: Much as I would have liked to compute the equity risk premium for every company, based upon its geographic operating exposure, the raw data did not lend itself easily to the computation. Consequently, I have used the equity risk premium of the country in which a company is headquartered to compute the equity risk premium for it.
- Relative Equity Risk: I stay with beta, notwithstanding the criticism of its effectiveness for two reasons. First, I use industry average betas, adjusted for leverage, rather than the company regression beta, because because the averages (I title them bottom up betas) are significantly better at explaining differences in returns across stocks. Second, and given my choice of industry average betas, none of the other relative risk measures come close, in terms of predictive ability. For individual companies, I do use the beta of their primary business as the beta of the company, because the raw data that I have does not allow for a breakdown into businesses.
- Corporate default risk: For the subset of the sample of companies with bond ratings, I use the S&P bond rating for the company to estimate the cost of debt. For the remaining companies, I use interest coverage ratios as a first measure to estimate synthetic ratings, and standard deviation in stock prices as back-up measure.
- Debt mix: I used the market capitalization to measure the market value of equity, and stayed with total debt (including lease debt) to estimate debt to capital and debt to equity ratios
 |
| Download industry costs of capital |
- Cost of capital calculation: The full cost of capital calculation is not complex, but it does require inputs about operating risk, leverage and default risk that can be hard to estimate or assess for young companies or companies with little history (operating and market). For those companies, I often use the distribution to estimate the cost of capital to use in valuing the company. Thus, when I valued Uber in June 2014, I used the cost of capital (12%) at the 90th percentile of US companies, in 2014, as Uber’s cost of capital. Not only did that remove a time consuming task from my to-do list, but it also allowed me to focus on the much more important questions of revenue growth and margins for a young company. Drawing on my fifth data update, where I talk about differences across currencies, this table can be easily modified into the currency of your choice, by adding differential inflation. Thus, if you are valuing an Indian IPO, in rupees, and you believe it is risky, at the start of 2025, adding an extra 2% (for the inflation differential between rupees and dollars in 2025) to the ninth decile of Indian costs of capital (12.08% in US dollars) will give you a 14.08% Indian rupee cost of capital.
- Fantasy hurdle rates: In my experience, many investors and companies make up hurdle rates, the former to value companies and the latter to use in investment analysis. These hurdle rates are either hopeful thinking on the part of investors who want to make that return or reflect inertia, where they were set in stone decades ago and have never been revisited. In the context of checking to see whether a valuation passes the 3P test (Is it possible? Is it plausible? Is it probable?), I do check the cost of capital used in the valuation. A valuation in January 2025, in US dollars, that uses a 15% cost of capital for a publicly traded company that is mature is fantasy (since it is in well in excess of the 90th percentile), and the rest of the valuation becomes moot.
- Time-varying hurdle rates: When valuing companies, I believe in maintaining consistency, and one of the places I would expect it to show up is in hurdle rates that change over time, as the company’s story changes. Thus, if you are valuing a money-losing and high growth company, you would expect its cost of capital to be high, at the start of the valuation, but as you build in expectations of lower growth and profitability in future years, I would expect the hurdle rate to decrease (from close to the ninth decile in the table above towards the median).
- Corporate hurdle rate: The notion that there is a corporate hurdle rate that can be used to assess investments across the company is a myth, and one with dangerous consequences. It plays out in all divisions in a multi-business company using the same (corporate) cost of capital and in acquisitions, where the acquiring firm’s cost of capital is used to value the target firm. The consequences are predictable and damaging, since with this practice, safe businesses will subsidize risky businesses, and over time, making the company riskier and worse off over time.
- Reality check on hurdle rates: All too often, I have heard CFOs of companies, when confronted with a cost of capital calculated using market risk parameters and the company’s risk profile, say that it looks too low, especially in the decade of low interest rates, or sometimes, too high, especially if they operate in an risky, high-interest rate environment. As I noted in the last section, making up hurdle rates (higher or lower than the market-conscious number) is almost never a good idea, since it violates the principle that you have live and operate in the world/market you are in, not the one you wished you were in.
- Hurdle rates are dynamic: In both corporate and investment settings, there is this almost desperate desire for stability in hurdle rates. I understand the pull of stability, since it is easier to run a business when hurdle rates are not volatile, but again, the market acts as a reality check. In a world of volatile interest rates and risk premia, using a cost of capital that is a constant is a sign of denial.
- Hurdle rates are not where business/valuation battles are won or lost: It is true that costs of capital are the D in a DCF, but they are not and should never be what makes or breaks a valuation. In my four decades of valuation, I have been badly mistaken many times, and the culprit almost always has been an error on forecasting growth, profitability or reinvestment (all of which lead into the cash flows), not the discount rate. In the same vein, I cannot think of a single great company that got to greatness because of its skill in finessing its cost of capital, and I know of plenty that are worth trillions of dollars, in spite of never having actively thought about how to optimize their costs of capital. It follows that if you are spending the bulk of your time in a capital budgeting or a valuation, estimating discount rates and debating risk premiums or betas, you have lost the script. If you are valuing a mature US company at the start of 2025, and you are in a hurry (and who isn’t?), you would be well served using a cost of capital of 8.35% (the median for US companies at the start of 2025) and spending your time assessing its growth and profit prospects, and coming back to tweak the cost of capital at the end, if you have the time.
- Data Update 1 for 2025: The Draw (and Danger) of Data!
- Data Update 2 for 2025: The Party continued for US Equities
- Data Update 3 for 2025: The times they are a’changin’!
- Data Update 4 for 2025: Interest Rates, Inflation and Central Banks!
- Data Update 5 for 2025: It’s a small world, after all!
- Data Update 6 for 2025: From Macro to Micro – The Hurdle Rate Question!
- Cost of capital, by industry grouping: US, Global, Emerging Markets, Japan, Europe, India, China)
- Cost of capital distribution, by industry
Paper links
Source: https://aswathdamodaran.blogspot.com/2025/02/data-update-6-for-2025-from-macro-to.html
Anyone can join.
Anyone can contribute.
Anyone can become informed about their world.
"United We Stand" Click Here To Create Your Personal Citizen Journalist Account Today, Be Sure To Invite Your Friends.
Before It’s News® is a community of individuals who report on what’s going on around them, from all around the world. Anyone can join. Anyone can contribute. Anyone can become informed about their world. "United We Stand" Click Here To Create Your Personal Citizen Journalist Account Today, Be Sure To Invite Your Friends.
LION'S MANE PRODUCT
Try Our Lion’s Mane WHOLE MIND Nootropic Blend 60 Capsules
Mushrooms are having a moment. One fabulous fungus in particular, lion’s mane, may help improve memory, depression and anxiety symptoms. They are also an excellent source of nutrients that show promise as a therapy for dementia, and other neurodegenerative diseases. If you’re living with anxiety or depression, you may be curious about all the therapy options out there — including the natural ones.Our Lion’s Mane WHOLE MIND Nootropic Blend has been formulated to utilize the potency of Lion’s mane but also include the benefits of four other Highly Beneficial Mushrooms. Synergistically, they work together to Build your health through improving cognitive function and immunity regardless of your age. Our Nootropic not only improves your Cognitive Function and Activates your Immune System, but it benefits growth of Essential Gut Flora, further enhancing your Vitality.
Our Formula includes: Lion’s Mane Mushrooms which Increase Brain Power through nerve growth, lessen anxiety, reduce depression, and improve concentration. Its an excellent adaptogen, promotes sleep and improves immunity. Shiitake Mushrooms which Fight cancer cells and infectious disease, boost the immune system, promotes brain function, and serves as a source of B vitamins. Maitake Mushrooms which regulate blood sugar levels of diabetics, reduce hypertension and boosts the immune system. Reishi Mushrooms which Fight inflammation, liver disease, fatigue, tumor growth and cancer. They Improve skin disorders and soothes digestive problems, stomach ulcers and leaky gut syndrome. Chaga Mushrooms which have anti-aging effects, boost immune function, improve stamina and athletic performance, even act as a natural aphrodisiac, fighting diabetes and improving liver function. Try Our Lion’s Mane WHOLE MIND Nootropic Blend 60 Capsules Today. Be 100% Satisfied or Receive a Full Money Back Guarantee. Order Yours Today by Following This Link.